5R Strategy – Reuse with RFID
Rethink, Recover, Repair, Reuse, Recycle. These are the 5 key pillars of a strategy to support circular economy in the textile industry, the 5R strategy.
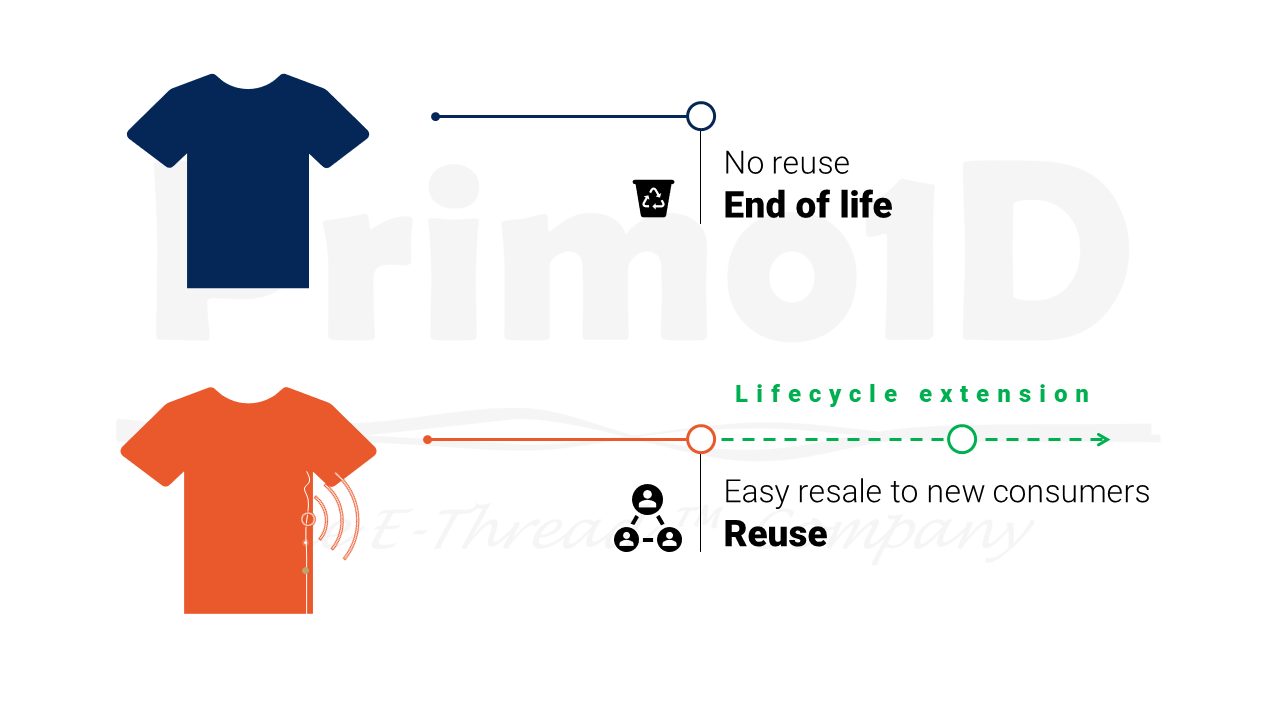
By reusing an article, on gives it a new life and delays its scrapping. Thus, it also reduces the need for new articles as well as energy consumption from recycling and destruction.
Reuse, what is it about?
May it be second-hand or renting, by reusing an article, consumers will wear garments already used by someone else before them. In a way, reusing articles makes it possible to redistribute them to other consumers instead of sending them to scrape.
Many examples of reuse already exist.
Second-hand retail articles
Second-hand scaled in France through citizen’s initiatives and associations. Recently, young companies also made it their main business model and fast fashion brands also took up second-hand use case to complete their offer with second-hand corners, sometime directly instore.
This new offer is an answer to already existing regulation in France and coming regulation in Europe.
Renting
Renting articles is another solution meeting reuse criteria. It enables consumers to get articles for a given time, without having to acquire it entirely, and to keep using it renter after renter. Beyond its added value in circular economy, renting meets other requirements: for example, it reduces the costs of some articles’ use when they are only occasionally worn (such as sports good). A French sports good retailer showed that rental business model leads to products lifespan extension and profits increase, meanwhile consumers expenses are divided by six compared to the ownership business model.
It should be noted that reuse can be considered as a way to recycle.
Embedded RFID in reuse business models
Reusing articles has its own limits, especially when they get too old or when their quality is degraded. Thereby, it must be decided whether the article can be reused or not; it is not rare that articles are thrown away based on quality drop prevention.
Undetachable embedded RFID tags enable garments lifecycle follow-up and information gathering to support decision-making in a durable and reliable way.
Beyond reuse or scrape decision-making, embedded RFID can also provide information to set second-hand clothes new prices (brand, production year, composition, etc.)
Embedded RFID offers another advantage, especially for brands, as it facilitates re-labeling processes of articles before reshelving.
Impacts
Consistently, reusing improves consumers environmental impacts:
- It decreases textile waste production;
- It limits our dependency to raw and virgin materials;
- It reduces energy consumption related to garments manufacturing and recycling;
- It minimizes waste incineration CO2 emissions;
- And also, it slows down methanation (methane synthesis) in landfilling areas.
Finally, reusing creates a new business reservoir for brands, as it optimizes the lifecycle and captures its added value.